In this section you will learn basic knowledge of CSS.
We will build upon your HTML page that you built in previous section, and make it soooo pretty.
Again we recommend using one of your fellow CodeKitten to go trough this together, as this is now the creative part of the internet. Working together will be so much more fun!
CSS: What is it?
CSS = Cascading Style Sheets
CSS is a "style sheet language" that lets you style the elements on your page.
CSS works in conjunction with HTML, but is not HTML itself.
CSS: What can it do?
All colored text, position, and size

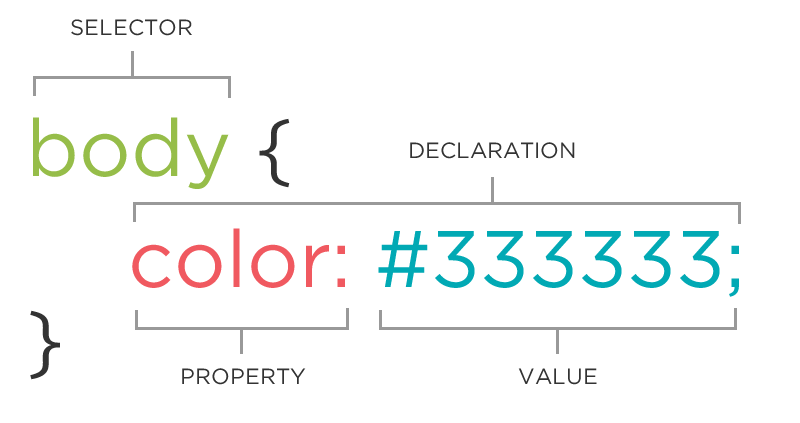
CSS: What does it look like?

The CSS rule
A block of CSS code is a rule. The rule starts with a selector. It has sets of properties and values. A property-value pair is a declaration.
selector {
property: value;
}
CSS syntax
Declarations: Property and value of style you plan use on HTML element. They end with a semicolon. Declaration groups are surrounded by curly brackets.
selector {
property: value;
property: value;
property: value;
}Selector: Elelment
p {
property: value;
}Selects all paragraph elements.
img {
property: value;
}Selects all image elements.
Selector: ID
#footer {
property: value;
}Selects all elements with an id of "footer".
The associated HTML.
<p id="footer">Copyright 2011</p>Selector: Class
.warning {
color: red;
}Selects all elements with a class of "warning".
The associated HTML.
<p class="warning">Run away!</p>IDs VS. Clasess
ID -- Should only apply to one element on a webpage. I.E. A webpage only has one footer. The "#" is how you tell CSS "this is an id."
Class -- Many elements can have the same class. I.E. There can be many warnings on one webpage. The "." is how you tell CSS "this is a class name."
Selector: position
p em {
color: yellow;
}Selects all em elements that are within a paragraph
The associated HTML.
<p>This is <em>important.</em></p>Property values
Each property can have one or more comma separated values.
p{
color: white;
background-color: red;
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
}Property: Color
The color property changes the color of the text.
p {
color: red;
color: #ff0000;
color: rgb(255, 0, 0);
}- Color name
- Hexadecimal value
- RGB value
The 17 standard colors are: aqua, black, blue, fuchsia, gray, grey, green, lime, maroon, navy, olive, purple, red, silver, teal, white, and yellow.
Property: Background-color
The background-color property changes the color of the background.
p {
background-color: black;
background-color: #000000;
background-color: rgb(0,0,0);
}Property: Font-family
The font-family property defines which font is used.
p {
font-family: "Times New Roman";
font-family: serif;
font-family: "Arial", sans-serif;
}- Specific font name
- Generic name
- Comma-separated list
Property: Font-size
The font-size property specifies the size of the font.
p {
font-size: 12px;
font-size: 1.5em;
font-size: 100%;
}- Pixels
- "em"
- Percentage
Property: Fonts (shorthand)
p {
font-style: italic;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 10px;
font-family: sans-serif;
}or
p {
font: italic bold 10px sans-serif;
}is the same.
Connection CSS to HTML
There is 3 ways to connect css to HTML
- "Inline"
- "Embedded"
- "External"
Connecting CSS to HTML: Inline
<p style="color:red">Some text.</p>Uses the HTML attribute style. It is difficult to use in large projects so it is not preferred way of doing CSS. Do it only if you rally have to.
Connecting CSS to HTML: Embedded
<head>
<style type="text/css">
p {
color: blue;
font-size: 12px;
}
</style>
</head>When the styling is put inside <head> element. It uses <style> tag.
The downside of this way is that it can only be used in one html file.
Connecting CSS to HTML: External or linked
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="style.css">
</head>This is most common and preferred way of using CSS as it acts like shared resource for several pages. The bonus with it is also that it has reduced file size & bandwidth, it is easy to maintain in larger projects.
Preferred by geeks everywhere!
CAT Action!
- Create a new .css file
- Add a link to the file in the head of the portfolio made last time
- Add styles to change the colors, background colors or fonts of different parts of the content
- Try using ids and classes to change specific elements ***
Cascading
Styles "cascade" down until changed. That means if you define a style for a tag in the begining of the file and then again at the end, the definition of the style at the bottom.
p{
color:blue;
font-family: 'Helvetica';
}
.red{
color:red;
}
#special{
font-family: Arial;
}<p>Paragraph</p>
<p class ="green">Paragraph</p>
<p class ="red">Paragraph</p>
<p class = "red" id ="special">Paragraph</p>CSS properties
Many CSS properties have self-explanatory names:
- background-color
- font-family
- font-size
- color
- width
- height
Here is a comprehensive list of all CSS properties